Pronunciation: (A se BUE toe lol HYE-droe-KLOR-ide)
Strength: 400 mg
Dosage Form: Capsules
Size: 100
NDC: 53746-0670-01
UPC: 3-5374667001-4
Each GTIN: 00353746670014
OTC/Rx: RX
TE Code: AB
Reference Brand: Sectral®
Status: Active
Case Qty / Min Order Qty: 24
Case GTIN: 50353746670019
Pill Size (inches): 0.9256 x 0.287
Pill Weight (mg): 615
Bottle Size (LxWxH inches): 2.3955 x 2.3955 x 4.401
Bottle Weight (g): 99.79
Case Size (LxWxH inches): 14.625 x 10.25 x 4.75
Case Weight (lbs): 5.90
Special Instructions: Keep this and all medication out of the reach of children. Keep tightly closed. Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
Product Shelf Life: 36 months
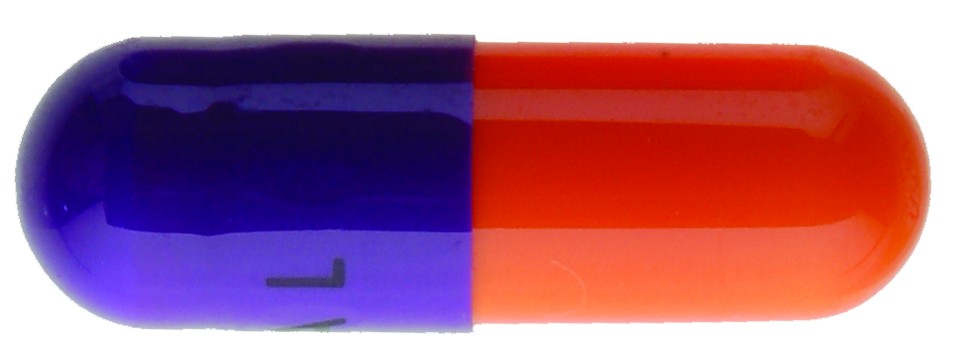
Shape: Capsule-shaped
Color: Bright orange opaque Body and lavender opaque cap
Imprint Markings: Body printed radially “670” with black ink and Cap printed radially “Amneal” with black ink
Allergens: Call (877) 835-5472 option 3 for any allergen questions.
Acebutolol HCl, 400mg USP
Si Disponible: Dispensado al Día Siguiente
Envío Gratis
Dentro de México
Requiere Receta Médica
Este Medicamento requiere prescripción médica de su médico, clínica, hospital o terapeuta.
Description
Product Overview
Acebutolol HCl is a selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor blocker (beta-blocker) used primarily to manage hypertension and certain types of heart rhythm disorders. It decreases the heart rate and reduces blood pressure, improving overall heart function and reducing the workload on the heart.Indications
Acebutolol HCl is indicated for the treatment of:- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): It can be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: Specifically indicated for the management of ventricular premature beats (VPBs), ventricular tachycardia, and other disturbances of cardiac rhythm.
Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Form: Oral tablets or capsules
- Standard Strengths: Commonly available in 200 mg and 400 mg doses.
- Administration:
- For hypertension, the usual starting dose is 400 mg daily, which may be administered once or divided into two doses (200 mg twice daily).
- For cardiac arrhythmias, the initial dose is generally 200 mg twice daily, which may be adjusted based on response and tolerance.
- It can be taken with or without food, but it is advisable to take it consistently at the same time each day.
Mechanism of Action
- Acebutolol HCl selectively blocks beta-1 adrenergic receptors, which are primarily located in the heart. By doing so, it decreases the heart rate, myocardial contractility, and cardiac output.
- It also exhibits intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), meaning it can mildly stimulate beta-adrenergic receptors, reducing the likelihood of severe bradycardia or a significant decrease in cardiac output, compared to non-selective beta-blockers.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract; bioavailability is about 40% due to first-pass metabolism.
- Onset of Action: Typically within 1–2 hours of oral administration.
- Metabolism: Metabolized in the liver to diacetolol, an active metabolite that also exhibits beta-blocking activity.
- Excretion: Primarily excreted via urine, with some fecal elimination.
Safety and Precautions
- Contraindications: Contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe bradycardia or heart block greater than first degree (without a pacemaker)
- Cardiogenic shock or overt cardiac failure
- Known hypersensitivity to Acebutolol or any of its components
- Warnings:
- Use with caution in patients with a history of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as it may exacerbate bronchospasm.
- May mask signs of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients.
- Abrupt discontinuation should be avoided due to the risk of withdrawal symptoms such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, or angina.
- Adjust dose in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Use with caution in pregnancy and not recommended during breastfeeding, as it may pass into breast milk.
Adverse Reactions
Common side effects may include:- Fatigue, dizziness, and headache
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (e.g., nausea, diarrhea)
- Mild hypotension
- Rash or other hypersensitivity reactions
- Less common but serious side effects include exacerbation of heart failure, bronchospasm, or conduction abnormalities.
Clinical Benefits
Clinical studies have shown that Acebutolol HCl:- Effectively lowers blood pressure and reduces the risk of cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients.
- Helps control abnormal heart rhythms, improving patient stability and reducing the risk of arrhythmia-related complications.
Storage
- Store at room temperature, protected from moisture and light.
- Keep out of reach of children.
Regulatory Classification
- Prescription-only Medicine: Requires a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider.
- Classified as a beta-1 selective adrenergic blocker with partial agonist activity (ISA).